Landscape Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide for Strategic Decision-Making
In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, organizations need to understand the context in which they operate to make informed decisions. A landscape analysis provides a structured approach to assess the external and internal factors that can impact an organization’s success. This comprehensive guide will explore the key components of a landscape analysis, its benefits, and how to conduct one effectively.
What is Landscape Analysis?
A landscape analysis is a systematic process of gathering and analyzing information about the external and internal environment of an organization. It aims to identify opportunities, threats, strengths, and weaknesses. By understanding the competitive landscape, market trends, technological advancements, and regulatory changes, organizations can develop strategies to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks.
The scope of a landscape analysis can vary depending on the organization’s goals and objectives. It can focus on a specific industry, market segment, or geographic region. The analysis typically involves collecting data from various sources, including market research reports, industry publications, government data, and competitor analysis.
Key Components of a Landscape Analysis
A comprehensive landscape analysis typically includes the following components:
External Analysis
The external analysis focuses on factors outside the organization that can impact its performance. These factors are often categorized using frameworks such as PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental) or Porter’s Five Forces.
- Political Factors: Government policies, regulations, and political stability can significantly impact businesses. For example, changes in trade policies or tax laws can create opportunities or threats for organizations.
- Economic Factors: Economic conditions such as inflation, interest rates, and unemployment rates can influence consumer spending and business investment. Understanding these factors is crucial for forecasting demand and making investment decisions.
- Social Factors: Social trends, cultural norms, and demographic changes can impact consumer preferences and behaviors. Organizations need to understand these factors to develop products and services that meet the needs of their target market.
- Technological Factors: Technological advancements can disrupt industries and create new opportunities. Organizations need to monitor technological trends and invest in innovation to stay competitive.
- Legal Factors: Laws and regulations related to employment, consumer protection, and environmental protection can impact business operations. Organizations need to comply with these laws to avoid legal liabilities.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental concerns such as climate change, resource scarcity, and pollution are increasingly important for businesses. Organizations need to adopt sustainable practices to minimize their environmental impact.
Internal Analysis
The internal analysis focuses on the organization’s strengths and weaknesses. This involves assessing the organization’s resources, capabilities, and processes. A common framework for internal analysis is the SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis.
- Strengths: Internal capabilities that give the organization a competitive advantage. Examples include strong brand reputation, innovative products, and efficient operations.
- Weaknesses: Internal limitations that hinder the organization’s performance. Examples include outdated technology, lack of skilled employees, and inefficient processes.
- Opportunities: External factors that the organization can leverage to its advantage. Examples include emerging markets, changing consumer preferences, and technological advancements.
- Threats: External factors that can negatively impact the organization’s performance. Examples include increasing competition, economic downturns, and regulatory changes.
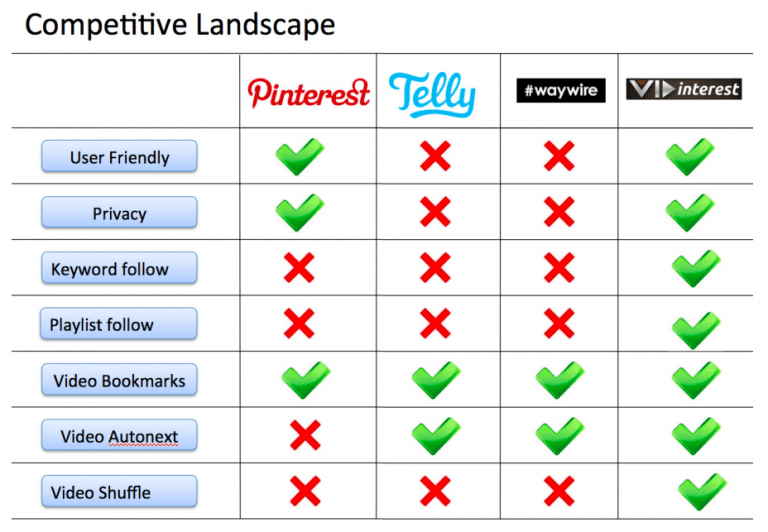
Competitive Analysis
A competitive analysis involves identifying and analyzing the organization’s key competitors. This includes understanding their strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market share. By understanding the competitive landscape, organizations can develop strategies to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive advantage.
Key aspects of a competitive analysis include:
- Identifying direct and indirect competitors
- Analyzing their products and services
- Assessing their pricing strategies
- Evaluating their marketing and sales efforts
- Understanding their strengths and weaknesses
Market Analysis
A market analysis involves understanding the size, growth, and trends of the market in which the organization operates. This includes analyzing market demographics, consumer behavior, and market segmentation. By understanding the market landscape, organizations can identify opportunities to expand their market share and develop new products and services.
Key aspects of a market analysis include:
- Determining the market size and growth rate
- Identifying key market segments
- Analyzing consumer demographics and psychographics
- Understanding consumer needs and preferences
- Assessing market trends and emerging technologies
Benefits of Conducting a Landscape Analysis
Conducting a landscape analysis offers several benefits for organizations:
- Informed Decision-Making: A landscape analysis provides valuable insights that can inform strategic decision-making. By understanding the external and internal environment, organizations can make more informed decisions about product development, market entry, and investment strategies.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying potential threats and risks, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate them. This can help organizations avoid costly mistakes and minimize the impact of adverse events.
- Opportunity Identification: A landscape analysis can help organizations identify new opportunities for growth and innovation. By understanding market trends and consumer needs, organizations can develop new products and services that meet the needs of their target market.
- Competitive Advantage: By understanding the competitive landscape, organizations can develop strategies to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive advantage. This can help organizations attract and retain customers, increase market share, and improve profitability.
- Strategic Planning: A landscape analysis provides a foundation for strategic planning. By understanding the external and internal environment, organizations can develop realistic goals and objectives, and develop strategies to achieve them.
How to Conduct a Landscape Analysis
Conducting a landscape analysis involves several steps:
- Define the Scope: Determine the scope of the analysis. This includes identifying the industry, market segment, or geographic region that will be analyzed.
- Gather Data: Collect data from various sources, including market research reports, industry publications, government data, and competitor analysis.
- Analyze Data: Analyze the data to identify trends, patterns, and insights. This includes using frameworks such as PESTLE, Porter’s Five Forces, and SWOT analysis.
- Identify Opportunities and Threats: Identify potential opportunities and threats based on the analysis.
- Develop Strategies: Develop strategies to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks.
- Monitor and Update: Continuously monitor the environment and update the analysis as needed. The business landscape is ever-changing, so it’s crucial to stay abreast of current trends.
Tools and Techniques for Landscape Analysis
Several tools and techniques can be used to conduct a landscape analysis:
- PESTLE Analysis: A framework for analyzing the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that can impact an organization.
- Porter’s Five Forces: A framework for analyzing the competitive intensity of an industry.
- SWOT Analysis: A framework for analyzing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of an organization.
- Competitor Analysis: A process of identifying and analyzing the organization’s key competitors.
- Market Research: A process of gathering and analyzing information about the market in which the organization operates.
- Scenario Planning: A process of developing and analyzing different scenarios to anticipate future events.
Examples of Landscape Analysis in Different Industries
A landscape analysis can be applied to various industries. Here are a few examples:
- Healthcare: A landscape analysis of the healthcare industry might focus on factors such as aging population, increasing healthcare costs, and technological advancements.
- Technology: A landscape analysis of the technology industry might focus on factors such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity.
- Retail: A landscape analysis of the retail industry might focus on factors such as e-commerce, changing consumer preferences, and supply chain disruptions.
- Finance: A landscape analysis of the finance industry might focus on factors such as interest rates, regulatory changes, and fintech innovations.
The Future of Landscape Analysis
As the business environment becomes increasingly complex and dynamic, the importance of landscape analysis will continue to grow. Organizations will need to adopt more sophisticated tools and techniques to understand the external and internal environment. The use of data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning will become increasingly common in landscape analysis.
Furthermore, organizations will need to integrate landscape analysis into their strategic planning process. This will involve developing a culture of continuous monitoring and analysis, and using insights from the analysis to inform decision-making at all levels of the organization. A thorough landscape analysis is no longer optional; it’s a necessity for survival and growth.
Conclusion
A landscape analysis is a critical tool for organizations to understand their environment and make informed decisions. By analyzing the external and internal factors that can impact their performance, organizations can identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and gain a competitive advantage. As the business environment continues to evolve, the importance of landscape analysis will only increase. Therefore, every organization must prioritize conducting a thorough and continuous landscape analysis to achieve sustainable success. [See also: Competitive Intelligence Strategies]
